- +91-9953164672,9810204946
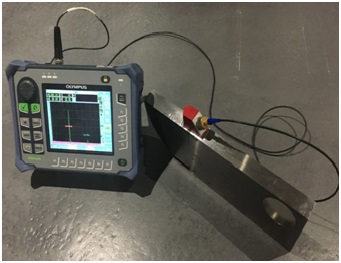
Ultra-high frequency sound is introduced into the part being inspected and if the sound hits a material with a different acoustic impedance (density and acoustic velocity), some of the sound will reflect back to the sending unit and can be presented on a visual display. The most common sound frequencies used in UT are between 1.0 and 10.0 MHz. The lower frequencies have greater penetrating power but less sensitivity while the higher frequencies don’t penetrate as deeply but can detect smaller indications. The two most commonly used types of sound waves used in industrial inspections are the compression (longitudinal) wave and the shear (transverse) wave. Because ultrasound will not travel through air, a liquid or gel called “couplant” is used between the face of the transducer and the surface of the part to allow the sound to be transmitted into the part. Ultrasonic testing is broadly divided into Pulse Echo (PE), Through Transmission (TT) and Time of Flight Diffraction (ToFD).